While Google has yet to reveal the exact algorithm it uses to rank websites, it announced a new ranking “signal” back in August. According to the Mountain View company, websites that use Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) over Secure Socket Layer (HTTPS) encrypted connections will now receive a slight boost in their search ranking.
Google uses hundreds of signals to determine when and where to rank websites, some of which include load times, domain age, content relevance, backlinks, bounce rate, and now HTTPS encryption. It’s important to note, however, that HTTPS is currently a “lightweight” signal, meaning it doesn’t yield the same level of influence over a site’s ranking as high-quality content.
Google broke the news about HTTPS being used as a ranking signal on the Webmaster Blog, saying the following:
“…over the past few months, we’ve been running tests taking into account whether sites use secure, encrypted connections as a signal in our search ranking algorithms. We’ve seen positive results, so we’re starting to use HTTPS as a ranking signal. For now, it’s only a very lightweight signal — affecting fewer than 1% of global queries, and carrying less weight than other signals such as high-quality content — while we give webmasters time to switch to HTTPS.”
Google Webmaster Central Video with John Mueller discussing HTTPS signal.
Go to 29:00 of video to watch the HTTPS topic.
In case this is your first time hearing about HTTPS, let me give you a brief explanation: it’s a method of creating a secure, encrypted connection to a server (website) and the visitor’s computer. By adding a 2048-bit SSL certificate, webmasters can reduce the risk of malicious attacks and prying eyes. This is particularly important for e-commerce sites and other websites which store customers’ sensitive financial data. When a client enters information such as their credit card number online, the information becomes encrypted between the customer’s computer and the website. Hackers that may be listening to this connection are not able to decipher the credit card number.
You can identify the presence of an encrypted connected by looking for the HTTPS prefix in a site’s address (unsecured sites are prefixed with HTTPS).
So, why is the Big G encouraging webmasters to switch from HTTP to HTTPS connections? Google has actively promoted the use HTTPS for several years now, automatically encrypting all user searches and Gmail accounts. On its blog, however, Google says the move aims to keep people safe.
But HTTP encryption isn’t foil-proof by any means. Earlier this year, the Heartbleed Bug was discovered in the OpenSSL cryptography library. This vulnerability allowed hackers and other individuals with malicious intent to gain access to secure servers by sending a pulse (hence the name) that mimicked the typical handshake process between a user and the server. It’s estimated that nearly half a million of the Internet ‘s secure web servers were vulnerable to the attack when Heartbleed was initially discovered. The vulnerability was soon fixed in a patch to the OpenSSL cryptography library, but it serves as a reminder that even encryption has its weaknesses.
Click Here is a link to more information from Google regarding securing your website with HTTPS
In additional News
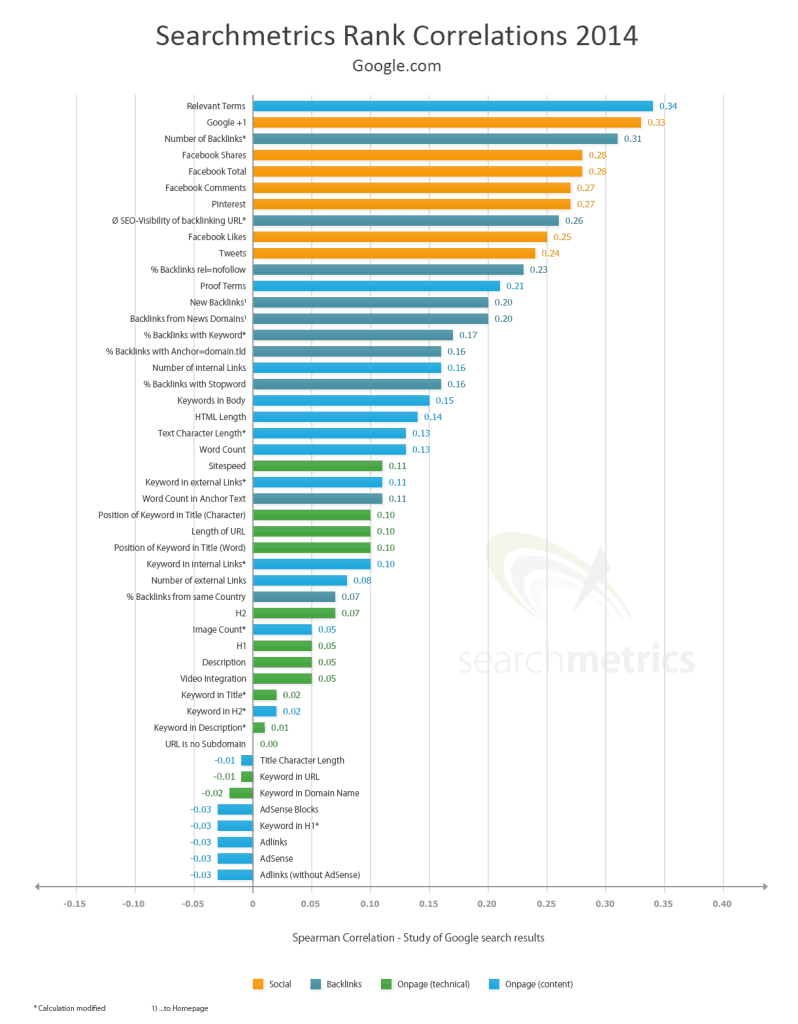
SearchMetrics.com has completed their 2014 Ranking Factor Study. Below is a screen shot of some of their findings. Keep in mind, Google does not publish their exact algorithm and continually adjusts their search results.
Or Contact WebWize At 713-416-7111
Before making a final decision on a Web Design Company, spend a few minutes on the phone with us.
About Glenn Brooks
Glenn Brooks is the founder of WebWize, Inc. WebWize has provided web design, development, hosting, SEO and email services since 1994. Glenn graduated from SWTSU with a degree in Commercial Art and worked in the advertising, marketing, and printing industries for 18 years before starting WebWize.